20 The Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic waves span an immerse range of frequencies from very long wavelength to extremely high energy with frequency 1023 Hz. 2 E 2 E t 2 E t.

Electromagnetic Waves Physics 4 Prepared By Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services At Ucsb Ppt Download
Electromagnetic waves or EM waves are waves that are created as a result of vibrations between an electric field and a magnetic field.

What is k in electromagnetic waves. Maxwell gave the basic idea of Electromagnetic radiations while Hertz experimentally confirmed the existence of an electromagnetic wave. The wave number is k 2 where is the wavelength of the wave. Different colors such waves are called monochromatic.
81 Cable waves Before getting into Maxwells equations and the wave equation for light lets do a warmup example and study the electromagnetic waves that propagate down a coaxial cable. This definition can be applied to the whole spectrum. We deal with both normal and non-normal angles of incidence.
C If the amplitude of the electric field is 600 V m what is the amplitude of the magnetic field. I am trying to understand the solution for electromagnetic plane waves in a conductor. In other words EM waves are composed of oscillating magnetic and electric fields.
What are the directions of the E and B vectors of the transmitted wave. If for a wave traveling in the x-direction E Ej then B Bk and j x k i. For electromagnetic radiation the wavenumber is proportional to the energy of the radiation or of the photon in quantum mechanics.
And solutions of the form. I understand the derivation of the wave equation. B Determine the values of and k.
Electromagnetic Waves in One Direction. Two other properties of electromagnetic waves that you may encounter from time to time are the wavenumber k and the angular frequency both of which are directly related to. You might know that light can be described as a flow of particles called photons orand as a wave depending on how you observe it.
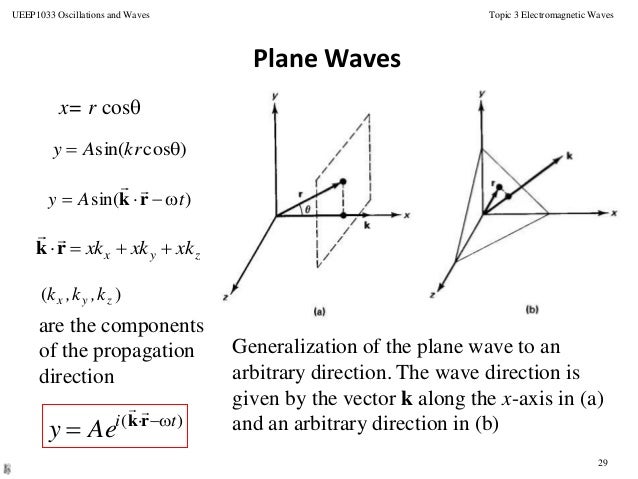
Then what most authors immediately do is say it admits plane wave solutions with a complex wave vector k k i . Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves. A 550nm harmonic electromagnetic wave whose electric field is in the direction z moves in the direction and in vacuum.
You can have waves in any direction. We have the differential equation for waves in the form. Electromagnetic waves are waves that are created as a result of variations of electric field and a magnetic field.
E z t E 0 e i k z t this is from Maxwells equations for a conductor. Solution of Electromagnetic Waves in Vacuum Contd i t o i t o B B e E E e Z Z k r k r Where E o and B o are the complex amplitudes of electric and magnetic fields and related to each other by relation 1 o k E o c B u Where is a propagation vectork. Electromagnetic wave propagating in the x-direction with the electric field E G pointing in the y-direction and the magnetic field B G in the z-direction as shown in Figure 1341 below.
The electric field associated with an electromagnetic wave in vacuum is given by Ei 40 cos kz-6x10 8 t where E z and t are in voltm metre and second respectively. K x t In the electromagnetic wave E is the electric field vector and B is the magnetic field vector. The wavelike description o.
An electromagnetic wave consists of an electric field defined as usual in terms of the force per charge on a stationary charge and a magnetic field defined in terms of the force per charge on a moving charge. Electromagnetic waves are formed when an electric field comes in contact with a magnetic field. Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves.
The electromagnetic field is assumed to be a function of only the x-coordinate and time. Or we can say that Electromagnetic waves are nothing but changing magnetic and electric fields. E in the i-direction and B in the j-direction O in the i-direction and B in.
The latter is a bit more involved due to the eects of polarization. A wave of single frequency is called a monochromatic wave. In fact for a continuous sinusoidal electromagnetic wave the average intensity I ave is given by.
In our example k is a vector in the x-direction. Figure 1341 A plane electromagnetic wave What we have here is an example of a plane wave since at any instant bothE andB G G are. ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES and glass.
They are hence known as electromagnetic waves. Electromagnetic waves are also known to be solutions of Maxwells equations. The value of wave vector k is.
2 E 2 E t 2 E t. There is no theoretical. The wavenumber k is simply the reciprocal of the wavelength given by the expression.
The wavenumber k is therefore the number of waves or cycles per unit distance. K 1 . A What is the frequency of the wave.
See Figure 1 Thus the energy carried and the intensity I of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to E 2 and B 2. In electromagnetic waves the amplitude is the maximum field strength of the electric and magnetic fields. When we expand the vector Laplacian we get.
Physics QA Library Suppose an electromagnetic plane wave propagating in vacuum in the k-direction has a polarization with the electric field in the i-direction immediately before it strikes a perfect conductor at normal incidence. Since the wavelength is measured in units of distance the units for wavenumber are 1 distance such as 1m 1cm or 1mm. 2 E 2 E x 2 E y 2 E z.
Bxt Bmaxcoskxt B x t B m a x cos. In a general case k is a vector.

5 1 4 Energy Flow Poynting Vector And Polarization

Solved Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell S Equations Allow For Chegg Com
Finding Real And Imaginary Parts Of The Complex Wave Number Physics Forums
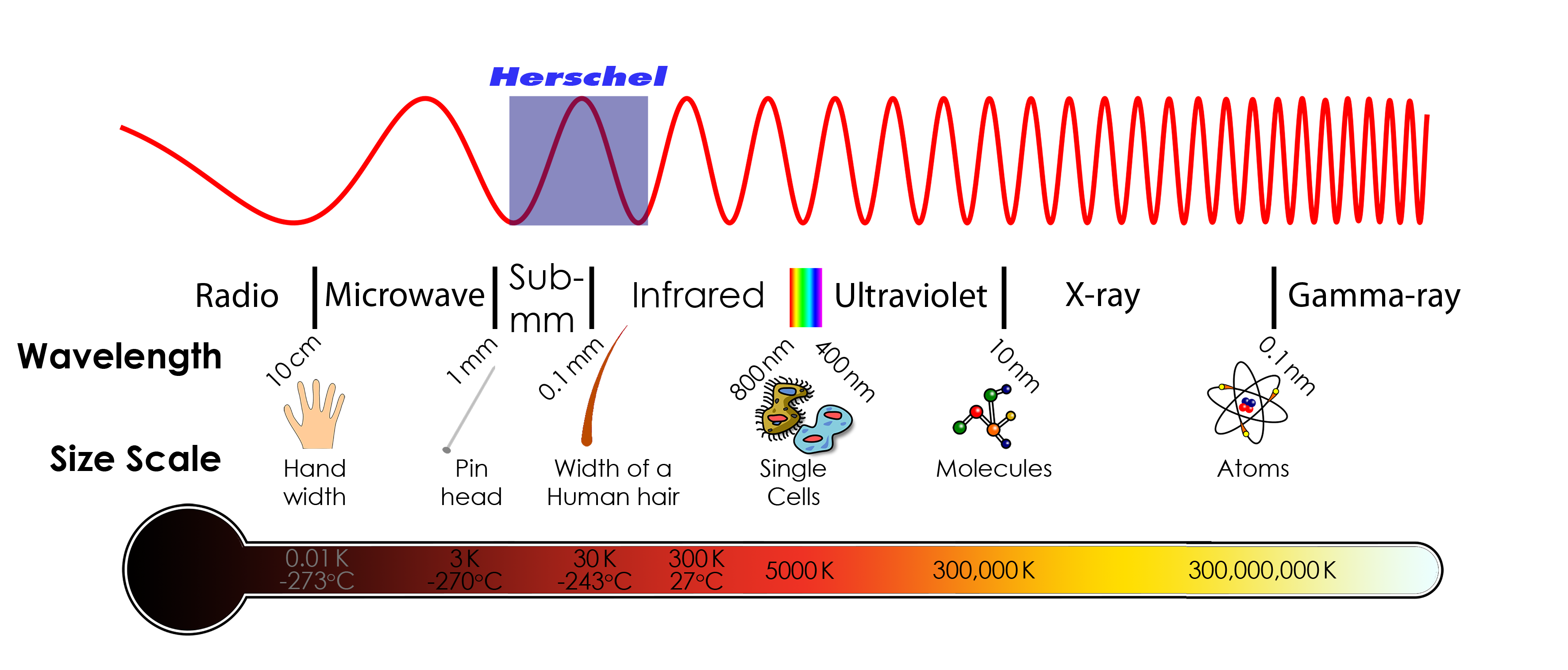
What Is Infrared Light Herschel Space Observatory
Spectrum Of Electromagnetic Waves With The Dispersion Em K And Of The Download Scientific Diagram

29 Maxwells Equations Electromagnetic Waves 1 2 3

Maxwell S Equations Differential Forms Electromagnetic Waves Y X Z E B And E K B K K Is The Direction Of The Wave Polarization Of Electromagnetic Ppt Download

Uy1 Electromagnetic Spectrum Sinusoidal Em Plane Waves Mini Physics Learn Physics

Electromagnetism Contents Review Of Maxwells Equations And Lorentz

The Electromagnetic Spectrum Astronomy

Electromagnetic Waves Ppt Download
Electromagnetic Waves Materials And Computation With Matlab 1st
Thermal Radiation Spectra Body Physics Motion To Metabolism

Post a Comment
Post a Comment